Redis rehash
- redis 渐进式rehash (incremental rehash)
- 1.何时触发rehash?
- 2.如何渐进rehash?
- 3. rehash 过程中的 get, set
- 4. 如何执行rehash的?
redis 渐进式rehash (incremental rehash)
参考:
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/358366217
- https://tech.meituan.com/2018/07/27/redis-rehash-practice-optimization.html
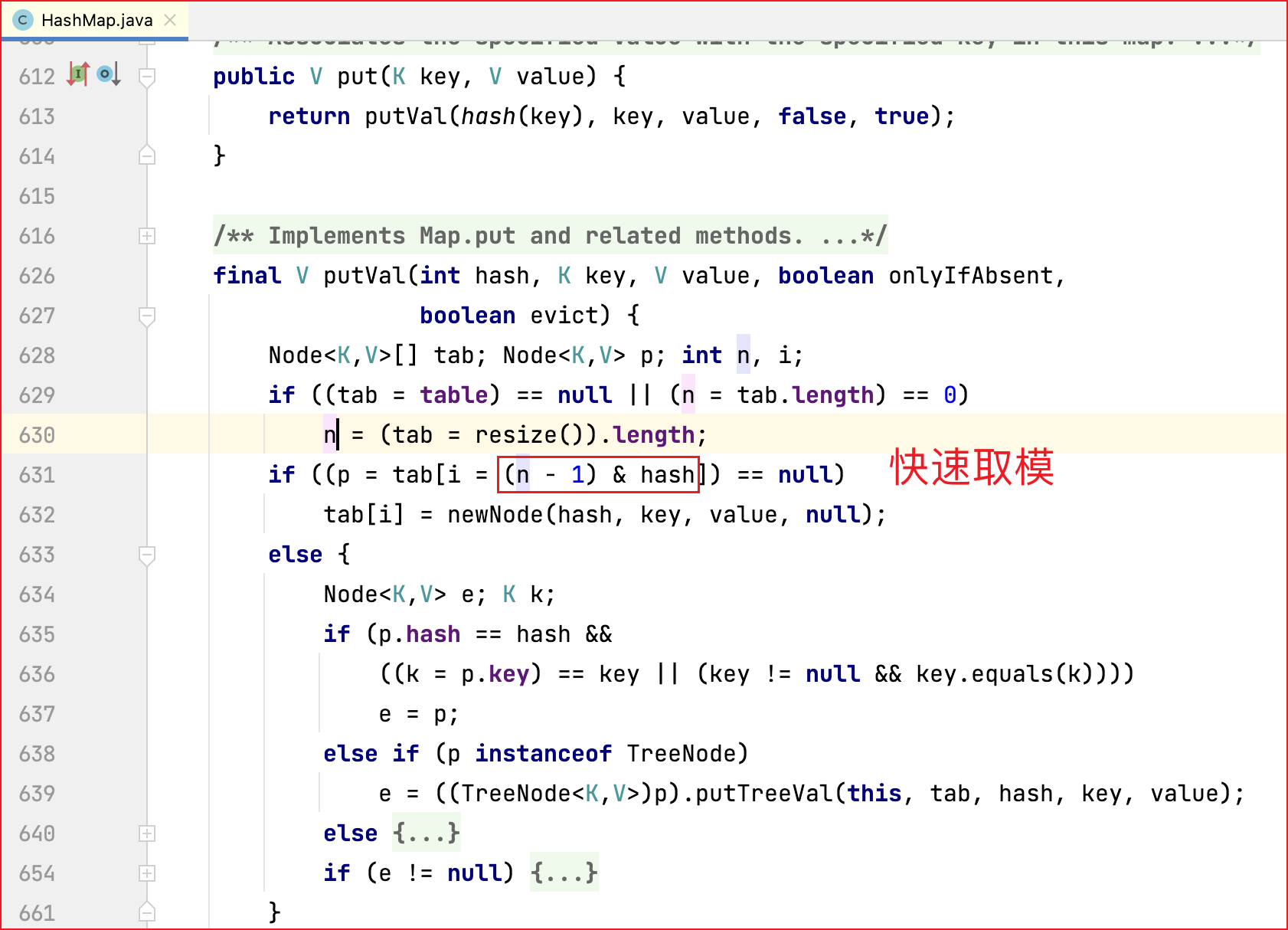
redis sizeMask vs java ju.hashmap 快速取模
二进制运算的特殊性质,
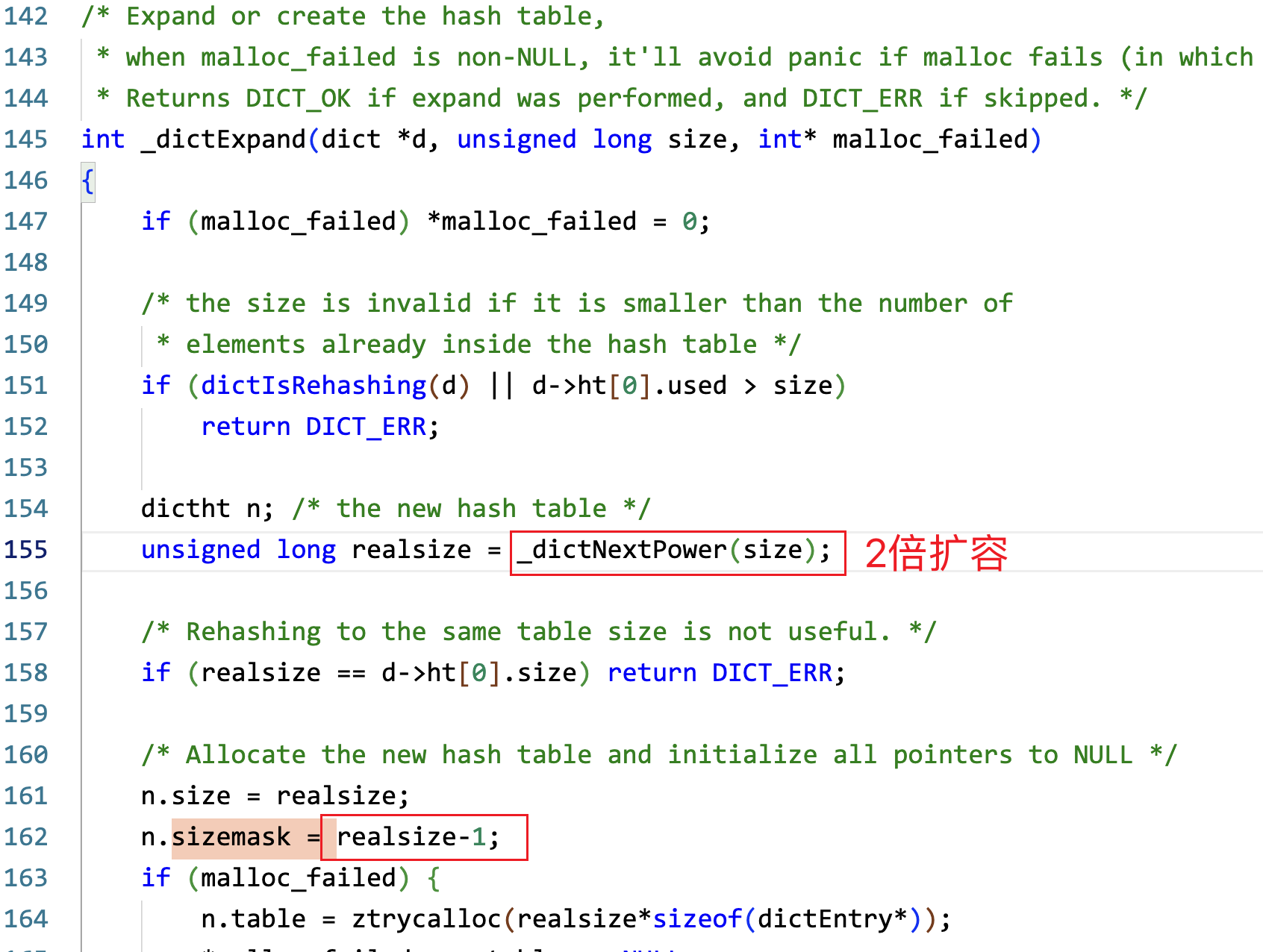
if n = 2^x, y%n == y&(n-1). 计算机的 二进制与运算 比取模运算要快不少, 所以redis 和 java hashmap 用与运算替换取模运算提高性能。
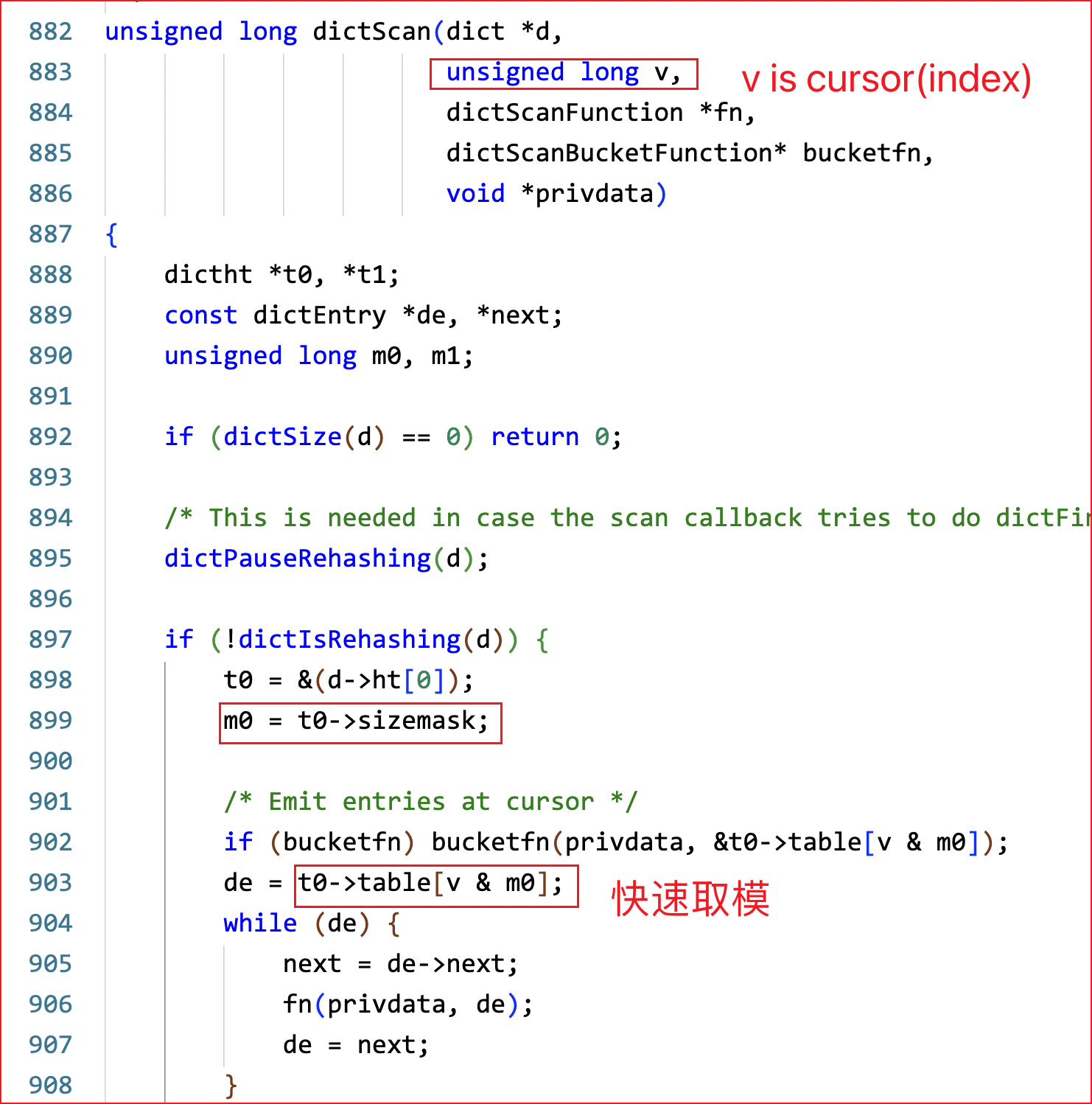
redis scan count
scan cursor count 10- scan 的返回可能会大于10
- redis是使用拉链法解决hash冲突的,当一个bucket 冲突严重, 有20个key时,这次scan会返回20个key
redis 的核心数据结构
// dict.h
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; // 拉链法解决key冲突
} dictEntry;
1.何时触发rehash?
static long _dictKeyIndex(), 查抄 key 对应的index时会触发 dictExpand(),设置 dict.rehashidx = 0
2.如何渐进rehash?
两个方式:
- 每个redis操作前会判定是否在rehash, 如果在rehash 会帮忙做一次 rehash ```c // dict.c static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) { if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1); }
int dictRehash(dict d, int n) { int empty_visits = n10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */ if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
}} ```
- redis server idle, 会执行批量的rehash,帮助快速完成rehash
int incrementallyRehash(int dbid) { /* Keys dictionary */ if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].dict)) { dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].dict,1); // 1ms,最多消耗1ms return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */ } }
3. rehash 过程中的 get, set
- get, delete 会两个table都查找一次
- add 只会在新的 table执行
4. 如何执行rehash的?
/* Performs N steps of incremental rehashing. Returns 1 if there are still
* keys to move from the old to the new hash table, otherwise 0 is returned.
*
* Note that a rehashing step consists in moving a bucket (that may have more
* than one key as we use chaining) from the old to the new hash table, however
* since part of the hash table may be composed of empty spaces, it is not
* guaranteed that this function will rehash even a single bucket, since it
* will visit at max N*10 empty buckets in total, otherwise the amount of
* work it does would be unbound and the function may block for a long time. */
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];//头插法
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}