0x01 - c#自问自答 - callback
1. call, callback, delegate, event handler是什么关系?
- FuncA call FuncB ,顺序执行
- FuncA call FuncB with callback 参数Func,执行完后,返回FuncA
- delegate是用于
封装命名或匿名方法的引用类型,类似于C++中的函数指针,但却是类型安全的。 - event handler 是callback的一种:主框架 =》事件 =》事件处理函数 =》返回主框架
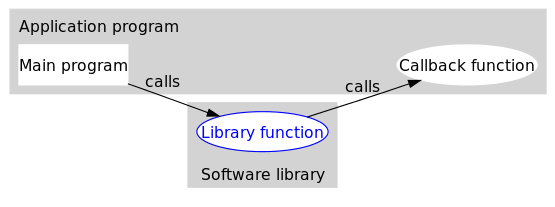
回调通常与原始调用者处于相同的抽象层
2. callback到底是什么?
Callbacks are extensibility points that allow a framework to call back into user code through a delegate. These delegates are usually passed to the framework through a parameter of a method.
callback 允许框架通过一个delegate 返回到用户代码中。
Events are a special case of callbacks that supports convenient and consistent syntax for supplying the delegate (an event handler). In addition, Visual Studio’s statement completion and designers provide help in using event-based APIs.
✓ CONSIDER using callbacks to allow users to provide custom code to be executed by the framework.
✓ CONSIDER using events to allow users to customize the behavior of a framework without the need for understanding object-oriented design.
✓ DO prefer events over plain callbacks, because they are more familiar to a broader range of developers and are integrated with Visual Studio statement completion.
X AVOID using callbacks in performance-sensitive APIs.
✓ DO use the new Func<...>, Action<...>, or Expression<...> types instead of custom delegates, when defining APIs with callbacks.
Func<...> and Action<...> represent generic delegates.
Expression<...> represents function definitions that can be compiled and subsequently invoked at runtime but can also be serialized and passed to remote processes.
✓ DO measure and understand performance implications of using Expression<...>, instead of using Func<...> and Action<...> delegates.
Expression<...> types are in most cases logically equivalent to Func<...> and Action<...> delegates.
The main difference between them is that the delegates are intended to be used in local process scenarios; expressions are intended for cases where it’s beneficial and possible to evaluate the expression in a remote process or machine.
✓ DO understand that by calling a delegate, you are executing arbitrary code and that could have security, correctness, and compatibility repercussions.
3. P/Invoke是什么,怎么用?
Platform Invocation Services (PInvoke) allows managed code to call unmanaged functions that are implemented in a DLL.
平台调用服务允许托管代码去调用dll中实现的非托管函数。
public delegate bool CallBack(int hwnd, int lParam);
public class EnumReportApp
{
[DllImport("user32")]
public static extern int EnumWindows(CallBack x, int y);
public static void Main()
{
CallBack myCallBack = new CallBack(EnumReportApp.Report);
EnumWindows(myCallBack, 1024);
// 1024这个参数经EnumWindows这个函数输入,
// 再经EnumWindows传送到callback中,
// callBack就可以处理
// callBack返回值,传送到EnumWindows中,false结束枚举窗口dll函数
// 代码执行桟==>重新回到Main函数中
Console.Read();
//执行流程:
// Main函数 --> Dll函数 --> CallBack函数 -->Main函数
}
public static bool Report(int hwnd, int lParam)
{
Console.Write("Window handle is ");
Console.WriteLine(hwnd+ "\t\t\t\t\t\t" + lParam);
if (hwnd > 100000)
return false;
return true;
}
}